Balanced Laminate B Matrix

Consequently the laminate extension and bending are uncoupled.
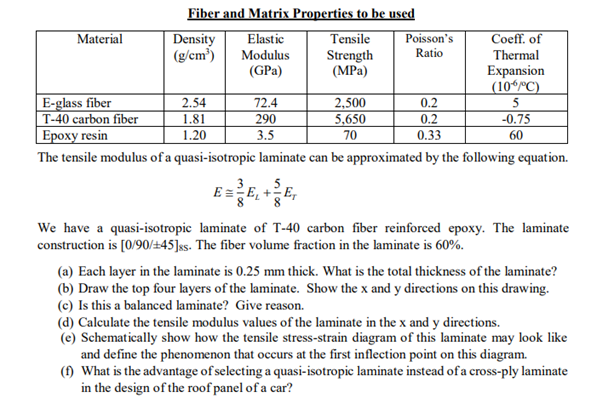
Balanced laminate b matrix. For the unbalanced laminate the a 16 and a 26 terms are non zero. Like angle ply laminates for balanced laminates a 16 a 26 0 and d 16 0 d. The laminate is equally stiff in the transverse direction and therefore a 22 a 11. This not only implies a11 a22 a16 a26 and a66 a11 a12 2 but also that these stiffnesses are independent of the angle of rotation of the laminate.
An example of a balanced laminate is 0 45 45 90 45 45 0 whereas an unbalanced laminate would be 0 45. A 45 45 s laminate is symmetric and therefore the coupling compliance matrix b is zero. The a matrix terms shown in figure 2 define an unbalanced laminate. In a balanced laminate the laminae with positive angles are balanced by equal laminae with negative angles.
The rectangles locate the a 16 and a 26 stiffness coefficients for each laminate. No shear extension coupling stacking sequence does not affect a matrix both laminates above have same tensile properties same a matrix 0 90 90 0 0 90 90 0 looks like i beam when bent looks not like i beam when bent on this axis. In balanced laminates for each off axis layer with a positive orientation angle there is an identical. For a symmetric laminate b 0 always for balanced laminates a 16 a 26 0 i e.
A balanced laminate is one that for every θ ply in the lay up there is an equivalent θ ply in the lay up. Balanced laminate balanced laminate a composite laminate in which all laminate at angles other than 0o and 90o occur only in pairs not necessarily adjacent and are symmetrical around the centerline. A laminate is called quasi isotropic if its extensional stiffness matrix a behaves like that of an isotropic material. If the laminate is not balanced and symmetric macro warpage will certainly occur during cool down.